Search
Installation of satellite TV
Advertising
Navigation
Main
Satellites
TV Package
HD Channels
Ultra HD Channels
BISS key
Coverage Maps
Sat Receivers
Installation of satellite TV
Satellite News
Contacts
Search
Installation of satellite TV
Advertising
Navigation
Installation and tuning of the direct focus antenna to the C-band, Yamal 401 |

Television, radio broadcasting and Internet from satellites is carried out in two main ranges - C (3500-4200 Mhz) and Ku (10700-12750 Mhz). Most antennas around the world are tuned to the Ku band. This is due to the fact that most satellites around the world broadcast in the Ku band. In the C-band, mostly Russian satellites broadcast such as Yamal (49'E, 90'E), Express-AM5 (140 E), ABS-2 (75'E). Antennas for receiving and C-band transmissions are large, therefore this range is less popular. For example, to receive the Ku band signal from the Yamal 401 90.0 ° E satellite, you can use a satellite antenna with a diameter of 0.9 - 1.2 meters, and to receive the C band, from the same satellite, it is desirable to use an antenna of at least 1.5, and preferably 1.8 - 2.0 meters However, the signal reception quality in the C-band is less dependent on the impact of meteorological conditions than in the Ku band. For example, Ku band reception is sharply degraded due to snow-covered antenna surfaces, clouds, or rain. At the same time, reception in the C-band is possible even on a fully snow-covered antenna, without degrading the image quality. Direct Focus AntennaFor receiving C-band signals, direct focus satellite antennas are mainly used, the diameters of which can be from 1.5 m to 3.7 m For direct focus antennas, the “mirror” has a parabolic shape. Because of this, the effect of a “direct beam” is achieved when the entire spectrum of radio waves incident on the mirror is reflected in the converter (see the figure below).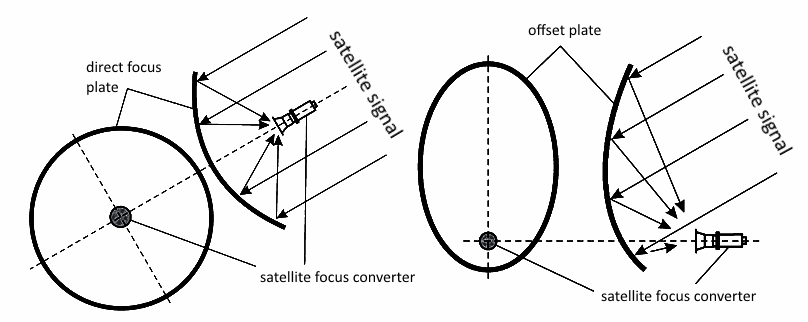
Focus lenses have their pros and cons. Since the satellite antenna converter is located in the middle, at the intersection of radio waves, it obscures the center of the antenna. Because of this, not all waves enter the converter. Because of this, it was necessary to increase the coverage area by 1.5-2 times and slightly increase the size of the emitter. Size solves another big question - the quality of reception, which offset antennas cannot boast of. The shape of the bend plays an important role: almost 90% of the area is used to collect and reflect the rays, while offset - only 70%. The main disadvantage of the direct focus dish is its location. When setting, the degree from the horizon is about 15-20% (for comparison, the offset satellite dish can generally stand upright or at most 5-7%). The slope contributes to the fact that all snow, water, dirt and leaves constantly settle on the reflector, thereby making reception difficult. Such television satellite dishes are inconvenient to mount on balconies or walls of buildings. To do this, I would have to make a long remote bracket, which is very not convenient. 
C-Band ConvertersThe converter (or LNB - Low Noise Block) is designed to convert the frequency of the C band (3.5 - 4.2 GHz) to an intermediate frequency of 900-2150 MHz for transmission with the least loss on the coaxial cable to the satellite receiver.
Specifications:
The local oscillator frequency for the C-band is set to 5150 MHz. For the C-band, 22 kHz is not necessary. Therefore, it’s absolutely all the same whether this signal will be or not. Polarization of convertersIn addition to the frequency spectrum (range), the converters differ in the type of polarization of the signal. Moreover, in one converter two types of polarization can be present at once.Here are two main types of converters: 1. Linear universal satellite converter (Universal) - in this type of converter there are two types of polarization: Linear Horizontal (H - Horisontal). Linear vertical (V - Vertical). 2. Circular satellite converter (Circular) - in this type of converter there are also two types of polarization: Circular Right (R - Right). Circular left (L - Leftl). Depolarizer The depolarizer allows you to convert the circular polarization of the signal from the satellite to linear, which the converter can take with greater efficiency. It is installed in linear polarization converters. Most often, a depolarizer is a dielectric plate in a converter waveguide. 
The material of the depolarizer is fluoroplastic, or, most often, fiberglass. You can use plates of light fiberglass, 6 mm thick, 35 mm wide, length - according to the internal size of the irradiator pipe. It is installed after searching and capturing the signal from the satellite into the irradiator tube at a position of 45 ° relative to the receiving probe (pin) in the head. If there are grooves in the waveguide for the head, a depolarizer is inserted into them. These are not the only possible materials and the form of depolarizers, but it is with such depolarizers that the most stable results and the least number of adjustments. 
If after installing the depolarizer the signal level has disappeared, or its level has dropped significantly - change the position of the depolarizer by 90 °, or change the polarization of the transponders in the tuner settings, vertical to horizontal and vice versa. NOTE: Some models of C-band converters allow you to increase the signal level with a non-standard position of the depolarizer, namely + 90 ° relative to the grooves. It is determined in a practical way. Tuning the direct focus antenna to the Yamal satellite 401 (201), 90 ° ENext, we will look at how to install and configure a 1.8 m straight-focus segmented satellite antenna to receive a signal from the Yamal satellite - 401, 90E (90 ° East). To receive a signal from the Yamal-201 satellite (90 ° East), a depolarizer plate, as described above, must be inserted into the converter. We select the installation location conditionally in such a way that the direction to the satellite — Novosibirsk — is a suitable place. The process of tuning the antenna in the C-band is not significantly different from tuning in the KU-band. To determine the coordinates of the direction to the satellite, we need to use the online calculator or another service to determine the elevation and azimuth. First you need to find out the geographical coordinates of your location, the name of the satellite. 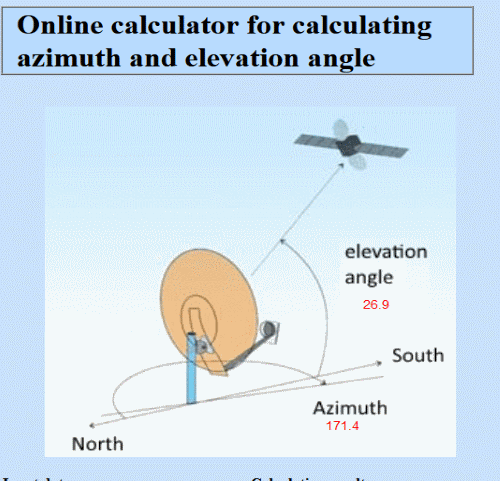
In our case, Novosibirsk: Coordinates of Novosibirsk in decimal degrees Latitude 55.0415 Longitude 82.9346 Substitute in the online calculator and calculate elevation angle: 26.9 ° bearing: 171.4 ° Next, we measure the azimuth using a compass, and the elevation angle using the goniometer as shown in the figure and proceed to configure the antenna. You can also navigate alongside standing antennas tuned to the same satellite. In the event that there are no antennas nearby, and you do not have a sufficiently accurate compass and goniometer, you can navigate in the search by the sun, whose position coincides with the position of the satellite at about 12 noon. 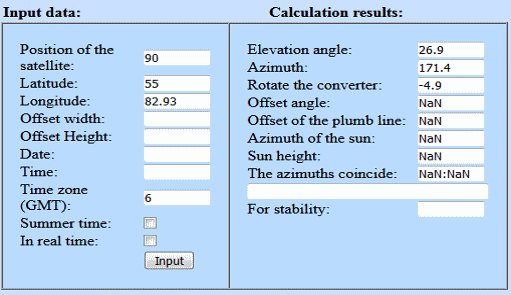
Search and capture of a signal from a satellite is carried out by the most powerful transponder. In the tuner menu, the converter local oscillator frequency is set to 5 150 MHz. The data of the strongest transponder is set. On Yamal, 90 ° E is the Gazkomovsky package.
Table No. 1. Satellite Transponder Parameters:
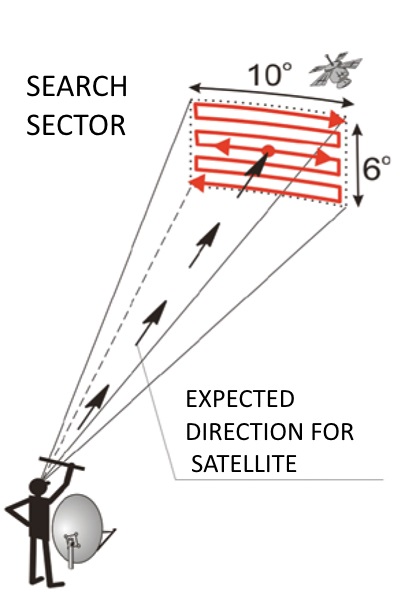
The broadcast parameters in the table are relevant at the time of writing and may change over time, so stay tuned for changes in the parameters in the table of frequencies and transponders. The setting is made according to the menu item "Signal strength" (Scan, etc.). Modern receivers usually have 2 measurement scales. First scale - "Level (Signal)" - shows the level of the inverter at the tuner input. Second - "Quality" - shows the level of the useful signal with the given parameters (frequency, speed and FEC). The level on the first scale includes both a useful signal from the satellite, and head noises, broadcast noises, the noise of all devices on the way from the head to the tuner. Most often, before connecting the head, the level is "0" and becomes greater than zero when it is connected. The initial search is carried out on the first scale. The level on it increases as you approach the satellite. The search is carried out by scanning the sector in which the satellite is supposed to be. It should be borne in mind that obstacles, such as a tree, a sun structure, also increase the signal level on the first scale. But through them it will be impossible to receive a satellite. When the tuner picks up a signal from the satellite, a level appears on the second scale - "Quality". Further tuning is carried out on a second scale to the maximum signal, the more percent the better. After tuning to the maximum signal, a depolarizer is inserted, its position is adjusted and proceed to Alignment. It should also be taken into account that the graduation of scales is different both on tuners of different manufacturers, and so often on different models of the same manufacturer. Therefore, it is incorrect to compare percentages of “Quality” of two different models of tuners. Fine tuning or adjustment is carried out by adjusting the position of the irradiator tube, its rotation, the position of the depolarizer, fine-tuning the direction of the antenna itself. All manipulations are performed in a circle a couple of times until the maximum signal is reached. After that, all other transponders are scanned into the tuner. After that, level control is performed on all channels. In the case of a low level on weak transponders, the antenna is adjusted again, already according to the level of weak channels. 
The scale at the end of the converter does not matter much, but simplified - if the satellite is in the south, then 0 - to the earth, the more to the east - right (by the hour) to 30, to the west, respectively, to the left to 30. I attach the irradiator with the converter to the extreme points, so that in the course of setting by turning the irradiator (for and against the hour) to find the maximum signal (changing focus). Enjoy watching! | |||||||||||||||||||